Understanding Medical Ultrasound
Health Capsule
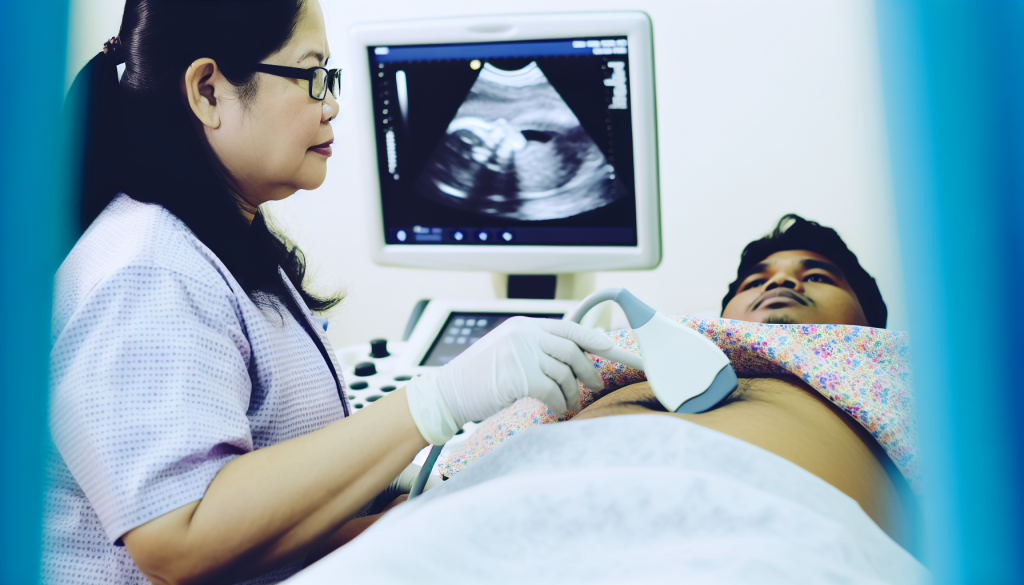
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive method that uses sound waves to produce visual representations of different areas within the body. It is commonly employed in prenatal care to monitor fetal development, measure heart rate, observe movements, and assess overall growth. Additionally, it is useful in examining other internal organs, including the kidneys, pelvic area, and thyroid gland.
When used for diagnostic purposes, ultrasound is widely regarded as safe. Unlike imaging methods such as X-rays or CT scans, it does not rely on radiation, making it a preferred option in various medical situations.
In a typical ultrasound procedure, a technician spreads a special gel on the skin to help transmit sound waves. Then, a small instrument called a transducer is moved across the targeted area. In some procedures, the device may be gently inserted into specific parts of the body, such as blood vessels or the rectum, for more detailed views.
The transducer sends out high-frequency sound waves that are inaudible to the human ear. As these waves bounce back from different tissues and structures, the device captures the echoes and converts them into images displayed on a monitor. Certain types of ultrasound can show real-time movement, allowing doctors to observe blood flow or heart activity. Others help detect abnormalities like tumors or scarring.
Ultrasound technology can also serve a therapeutic role. The sound waves may be used to break down kidney stones or dissolve blood clots, allowing them to pass naturally through the body. This dual function makes ultrasound a valuable tool in both diagnosis and treatment.

